|
1 |
Load resistance |
|
2 |
Intensity of Sunlight |
|
3 |
Cell temperature |
|
4 |
Shading |
Load Resistance
The variation of load (resistance) causes the modules voltage to change affecting panel efficiency and current output. When possible, system designers should ensure that the PV system operates at voltages close to the maximum power point of the array. If a load's resistance is well matched to a module's I-V curve, the module will operate at or near the maximum power point, resulting in the highest possible efficiency.
As the load's resistance increases, the module will operate at voltages higher than the maximum power point, causing efficiency and current output to decrease. Conversely, as module voltage drops below the maximum power point, the efficiency of the module decreases.
Intensity of the Sun
A Solar panel's current output is proportional to the intensity of solar energy to which it is exposed. More intense sunlight will result in greater module output. As shown below, as the sunlight level drops, the shape of the I-V curve remains the same, but it shifts downward indicating lower current output. Voltage is not changed appreciably by variations in sunlight intensity.
Cell Temperature
Under STC test conditions, as the cell temperature rises above the standard operating temperature of 25 degrees C, a solar panel operates less efficiently and the voltage decreases. As illustrated below, as cell temperature rises above 25 degrees C (cell temperature, not ambient air temperature), the shape of the I-V curve remains the same, but it shifts to the left at higher cell temperatures indicating lower voltage output.
A good installation should allow air flow under and over the modules to remove heat to avoid high cell temperatures.
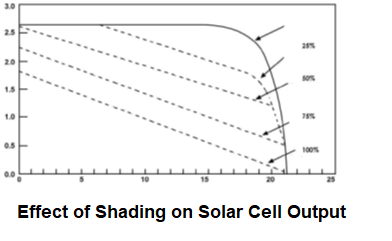
Shading
Shading affects the output of a solar panel. Even partial shading of photovoltaic modules will result in a dramatic output reduction. Some modules are more affected by shading than others. The illustration below shows the extreme effect of shading on one cell of a crystalline cell module.